Mapper Skill
Transforming Your Data
In your Mattr workflows, data often flows from one step to the next. But sometimes, the way data comes out of one system (or Skill) isn't quite the way another system (or Skill) needs it. For example, one system might call a customer's first name "Name," while another expects it as "FirstName."
The Mapper Skill is your workflow's data translator! It's used to transform and map data from its original "source" format to a new "target" format. This is super useful for renaming fields, changing data types, or setting default values, ensuring your data is always perfectly prepared for the next step.
Standardizing Payment Gateway Outputs for a Database
Imagine your workflow integrates with multiple payment gateways (e.g., PayPal, Stripe, a custom bank API). Each gateway might send payment confirmation details in a slightly different format. For instance, one might use txn_id for the transaction ID, while another uses payment_ref. Before storing this information in your internal database, you want to standardize it to a single field name, like transactionId.
The Challenge
Different payment gateways provide transaction details with varying field names, making it difficult to consistently store and analyze this data in your database.
The Solution
By using a Mapper Skill, you can take the unique output from each payment gateway and transform it into a standardized format. This ensures that no matter which gateway processed the payment, your database always receives consistent field names.
Setting Up the Mapper Skill
Let's walk through how to set up this Skill to standardize transaction IDs from different payment gateways.
Locate the Skill: Drag and drop the Mapper Skill onto your Workflow Builder canvas. Place it in your workflow immediately after the skill that receives the payment confirmation (e.g., an "API Call Node" that integrates with PayPal, Stripe, etc.). You'll likely have multiple Mapper Skills, one for each payment gateway's specific output.
Configure "Mappings": This is where you define how your data should be transformed.
Click on the Mapper Skill to open its configuration panel.
In the "Mappings" section, you'll add rules for each piece of data you want to transform. Each rule needs:
Target: The new name you want for the field (e.g., transactionId).
Type: The expected data type (e.g., string, number, date, any). This helps ensure data consistency.
Source: The original name of the field from the previous skill's output (e.g., $input.data.paypal_txn_id).
Default Value (Optional): If the Source field might sometimes be missing, you can provide a Default Value (e.g., N/A) to ensure the Target field always has a value.
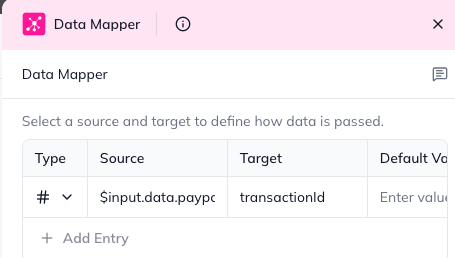
Example Mappings for Payment Gateways:
For PayPal Output:
Target: transactionId, Type: string, Source: $input.data.paypal_txn_id
Target: paymentAmount, Type: number, Source: $input.data.amount
For Stripe Output:
Target: transactionId, Type: string, Source: $input.data.stripe_payment_ref
Target: paymentAmount, Type: number, Source: $input.data.total_amount
Optional: "Name" and "Description": You can give your Mapper Skill a clear name (e.g., "Standardize PayPal Output") and a description for better workflow clarity.
Understanding the Outcome (Skill Output)
After the Mapper Skill runs, it provides a new data object with all your transformed fields, ready for the next step in your workflow (e.g., storing in your database).
data: This is the most important output. It's a new object containing all the fields you defined in your "Mappings," with their new names and types.
Example Input (from PayPal):
JSON
{
"paypal_txn_id": "PAY12345",
"amount": 100.50,
"currency": "USD"
}
Example Output (after Mapper Skill):
JSON
{
"transactionId": "PAY12345",
"paymentAmount": 100.50
}
statusCode: A number indicating the result of the mapping attempt:
200: Success – Data mapped successfully.
400: Bad Request – Invalid mapping syntax or an empty target field.
422: Unprocessable Entity – A source field was not found, and no default value was provided.
error: A string with a descriptive error message. This will be null if the statusCode is 200.
By using the Mapper Skill, you ensure that your data is always in the right format for every step of your workflow, making integrations smoother and data analysis more consistent!
Last updated